Overview Of Digital Currency – Final Part: Digital Currency Model Of Vietnamese Central Bank (CBDC)
12 Nov, 2021
It is the experience of developing digital currencies in other countries that points out the crucial participation of commercial banks as a bridge for CBDC-currency effective issuance into circulation. The development and launch of a national digital currency will become even more urgent in the future when the majority of countries around the world have implemented digital currencies.

CBDCs should be stablecoins – “sovereign” stable coins
Cryptographic technology use by private digital currencies today plays an important element in monetary policy management; in other words, the currency sovereignty does not belong to Central bank; rather, the decentralized computer network. This fact will make it very difficult for monetary policy conduction in case of the necessity to increase or decrease the urgent currency supply. In a pure cryptographic system, currency supply is determined by Algorithms and cannot be altered without the consensus from the majority of computers. Some countries, due to the nature that the blockchain must be open and governed by many separate entities - an important issue in this technology, have initiated on combining cryptocurrencies with sovereign currencies.

Issuing CBDCs as stablecoins avoids the risk of financial system destabilizing risk because of private currency flood
A sovereign cryptocurrency is more likely to closely resemble a fiat-stable digital currency, commonly known as a stablecoin. These coins have been existing and are processed in the blockchain network; however, its value is pegged to the fiat currency of a particular country.
One typical example is Tether (USDT), the world's top stablecoin within market capitalization at the time this podcast is being scripted. Each Tether unit is “pegged 1:1 to US dollar” and is “always valued by Tether at $1”. Consequently, the “stability” of this coin (if this description is to be eligible) relies on “reserves” of assets including “cash and cash equivalents”, which may include “other assets and receivables from loans made by Tether to 3rd parties”. The numbers in Tether's assurance disclosure are periodically audited by a reputable auditing firm in the market. The fact that, Tether coin, concurrently, does not need to set up its own blockchain system but arranged "symbiotically" with other powerful blockchains already available on the market like Ethereum or TronX boosts Tether quickly become a popular stablecoin due to the unnecessity in creating a private blockchain network.
The most important factor for a stablecoin is the transparency of the promise of “a 1:1 swap with fiat”. If the issuer is Central bank, this factor will be easily performed without any necessity for periodic audit conduction like Tether. Issuing CBDCs as stablecoins avoids the risk of financial system destabilizing because of private currency flood.
Role allocation towards commercial banks in Digital currency system
The idea of a new digital-currency generation initiated is to eliminate financial intermediaries (e.g. commercial banks), to reduce transaction costs and to limit third-party intervention in transactions. In terms cryptocurrency developers’ hypothesis: if the currency is fully digitized, the traditional role of commercial banks will gradually fade or, even, disappear from the modern financial system. All traditional activities of commercial banks (listing as: mobilization - lending, payment services and so on) will be replaced by "smart contracts" with almost-absolute accuracy and trustworthiness. Commercial banks will have to allocate resources with challenges to survive and develop in the new era when digital financial services are free and financial data is transparent.
The fact that the role of commercial banks in the new era can become transaction nodes of the blockchain system will validate transactions and be rewarded for their performance with new coins. Theoretically, commercial banks are acting as intermediaries for monetary policy implementation towards monetary-supply re-distribution; in fact; they, in reality, will shoulder the role of technical foundation for the new monetary system. Currency printing cost will be replaced by that of cryptographic-system monitoring and improvement as well as that of algorithm installation on blockchain network. Commercial banks will act as primary nodes (core nodes) whereas financial service providers as secondary nodes approaching the end-users. A digital currency system that ensures a safe transition from traditional 2-level monetary system (Central bank and commercial bank) should be encouraged to develop more in the context of potential risks related to the technical aspect of the blockchain system.
Optimal algorithm perfection towards monetary policy
Within cryptocurrency contexts, all data regarding spending, investment, interest rates, exchange rates as well as all big data related to one economy’s financial situation are updated as soon as possible. That creates a great motivation for a "smart" monetary policy design that automatically adjusts to money supply and demand as well as potential risks. An economy with an "automatic" monetary policy will help its financial system be stable and self-balanced under the supervision from Central bank with strengthened transparency, independence and management efficiency.
Multi-target monetary policy is often a defect of traditional economics as it is difficult for the operator to make decisions in case of diverse variable fluctuations in this economy. A digital currency system will help regulate the money supply in a rhythmic and appropriate way, in accordance with a pre-programmed and widely publicized algorithm besides network supervision - a modern monetary system capable of solving multiple equilibrium equations and optimization problems concurrently quickly and accurately in comparison to human subjectivity.
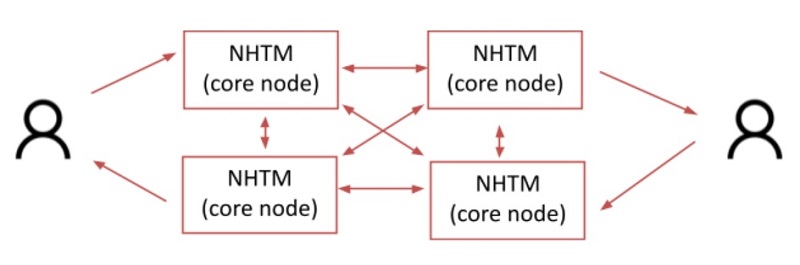
CBDC Distribution Model (Source: Author)
Liberalization betterment of microfinance services
One genuine power of the new cryptocurrency generation is unleashing non-traditional business ideas with the help of “smart contracts”. All transactions in the economy are pre-programmed without human intervention or extreme trust; in which, microfinance ideas will be implemented quickly and efficiently. Strong microfinance development will accelerate financial development and directly promote economic growth. Can only this prospect be achieved if entrance barriers into the financial markets are removed, the regulatory framework is clearly regulated and fraudulent and criminal activities are monitored by available mechanisms.
One initial concern of governments around the world was that cryptocurrency anonymity could facilitate illegal activities and laundering. However, these doubts were quickly erased when these governments understood that the digital currency system, actually, has anti-crime features. Since all transaction data is permanently stored in the blockchain, investigators can conduct tracing to track down suspicious transactions, even, to recover exhibits. In September 2013, thanks to tracing illegal transactions, US FBI arrested the drug lord and recovered nearly $ 9.5 billion worth of illegal bitcoins.
Sandbox mechanisms (experimental) should be encouraged for businesses to participate in cryptocurrency system operation. Legal provisions will be adjusted after the pilot process for creating a healthy and sustainable development environment towards CBDC digital currency. Typical applications of cryptocurrency technology should be widely fostered so that CBDC application can goes deeper into social life, helping to accelerate digital transformation for the real economy.
Conclusion
The intimate relationship between technology, currency and payment systems has been linked since the earliest days of human civilization. Over the past two decades, however, technology has reshaped money and payment systems at an unprecedented rate and speed. New generation digital currencies have challenged policymakers and regulators globally, representing a real threat to the traditional and slow to innovate financial system. However, this is an opportunity for the developing countries to revolutionize their monetary systems towards taking a shortcut to welcome a new era: the time that everything is digitally converted.
Among CBDC implementations discussed above, the key parameters in choosing a particular cryptocurrency model should be determined by effectiveness and safety, supporting the decisions from Central banks and regulators. According to this model, stable currencies (stablecoins) are likely to be the core model for Central bank in building digital currencies in each country and region. Experiences in developing digital currencies at other countries indicate that there should be the participation of commercial banks as a bridge for the effective issuance of CBDC currency into circulation; besides, it is necessary to develop a market to use CBDCs for people to get familiar with how to use cryptocurrencies. The development and the launch of a national digital currency will become even more urgent in the future when the majority of countries around the world have started to deploy digital currencies; if not, the price for our reluctance to change and improve would be the prospect of being left behind in the economy as well as influenced in the new digital economic community.
Please refer to the full research “Digital currency and new global currency-generation system” by Author group here.
Author group: PhD. Lê Đạt Chí, MA. Trương Trung Tài, MA. Nguyễn Triều Đông, (Faculty of Finance – UEH School of Management).
This sharing is attached with Series of Spreading research and applied knowledge by UEH. We would like to invite Dear readers to follow Knowledge News ECONOMICS NUMBER #12: TOWARDS BEING SMART UNIVERSITY THROUGH COMPREHENSIVE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION: ONE REPRESENTATIVE CASE OF UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS HO CHI MINH CITY.
News, photos by: Author group, Department of Marketing and Communication.